In a sense AVLock can be compared with one or more switches for protecting access to the application. Here are some of the most common protection schemes that could be implemented through AVLock SIMPLE. Please note that schemes A..G uses only one key to implement the protection unlike the scheme H which uses three different keys:
Symbols used in schemes
Scheme A
This is the simplest scheme where AVLock activate / deactivate the application according to their registration status:
|
Pseudo code:
If AVLock is registered then Run the application. |
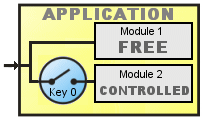
Scheme B
This scheme never block the access to the application and have a module of free access and other controlled by AVLock:
|
Pseudo code:
Run the application If button1 clicked then run Module1. If button2 clicked and registered then run Module2.
|
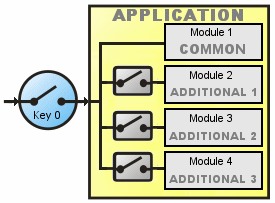
Scheme C
This scheme only allow access to the application when AVLock is registered. Also have a module of common access and other three controlled by AVLock with the Values field used as switches:
|
Pseudo code:
If AVLock is registered then Run the application If button1 clicked then run Module1. If button2 clicked and bit 1 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module2. If button3 clicked and bit 2 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module3. If button4 clicked and bit 3 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module4. |
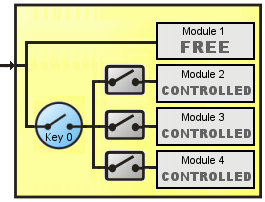
Scheme D
This scheme never block the access to the application and have a module of free access and other three controlled by AVLock with the Values field used as switches:
|
Pseudo code:
Run the application If button1 clicked then run Module1. If AVLock is registered then If button2 clicked and bit 1 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module2. If button3 clicked and bit 2 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module3. If button4 clicked and bit 3 of the Value1 field is 1 then run Module4.
|
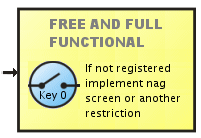
Scheme E
This scheme allow free access to the whole application, totally free and full functional. However, if the user is not registered then periodically show a nag screen or another design in order to encourage the user to register your application.
|
Pseudo code:
Run the application If not registered then show occasionally a nag screen or implement some delay or another design in order to motive to the user to register your application.
|
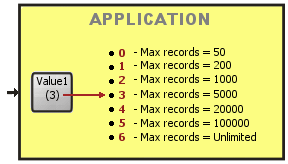
Scheme F
This may be a database application where you restrict the number of record allowed according a scale. The field Value1 is used as a selector to determine the value into the scale:
|
Pseudo code:
Run the application case Value1 of 0 : maxrecords := 50; 1 : maxrecords := 200; 3 : maxrecords := 1000; . . . .
|
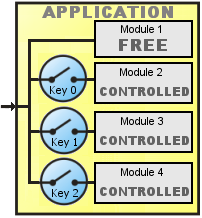
Scheme G
This scheme never block the access to the application and have a module of free access and other 3 controlled by AVLock. Like scheme C, but here uses three different keys, one for each controlled module:
|
Pseudo code:
Run the application If button1 clicked then run Module1. If button2 clicked and key 0 registered then run Module2. If button3 clicked and key 1 registered then run Module3. If button4 clicked and key 2 registered then run Module4.
|
This is not a definitive list. You could imagine and implement several other schemes for your real implementation.